Contents
- Anticoagulation Lab Tests at UW Medicine
- Anti-Xa Activity (Heparin Activity)
- Apixaban Assay (APIXN1)
- Chromogenic Factor X (CHRF10)
- Dabigatran Assay (DABIGL)
- Direct Oral Anticoagulant Screen (DOASP1)
- Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Assay (DTI) 1
- Fondaparinux Assay (FNDXT)
- INR Point-of-Care Testing (Rapid INR; PRORPD)
- Rivaroxaban Assay (RIVAR1)
Anticoagulation Lab Tests at UW Medicine
| Description | Order Code | Specimen Collection | Availability | Turn-Around Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Xa Based Tests | ||||
| anti-Xa for heparin | HIXA | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 24/7 | 30min STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4 hrs ROUTINE |
| anti-Xa for LMWH | LMWXA | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 24/7 | 30min STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4hrs ROUTINE |
| anti-Xa for apixaban level | APIXN1 | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 7am to 4pm daily | 1hr STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4hrs ROUTINE Off hours with Lab Medicine Resident approval |
| anti-Xa for fondaparinux level | FNDXT | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 7am to 4pm daily | 1hr STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4hrs ROUTINE Off hours with Lab Medicine Resident approval |
| anti-Xa for rivaroxaban level | RIVAR1 | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 7am to 4pm daily | 1hr STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4 hrs ROUTINE Off hours with Lab Medicine Resident approval |
| Coagulation Based Tests | ||||
| dabigatran level | DABIGL | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 7am to 4pm daily | 1hr STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4hrs ROUTINE Off hours with Lab Medicine Resident approval |
| direct oral anticoagulant screen (Combined thrombin time and direct Xa inhibitor screen) |
DOASP1 | 3ml or 5ml blue top tube | 24/7, sent as part of EMERGENCY STROKE PANEL | 30min STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4hrs ROUTINE |
| direct thrombin inhibitor assay (Plasma-diluted thrombin time) |
DTI | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 24/7 | 1hr STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4 hrs ROUTINE |
| Factor X Tests | ||||
| chromogenic factor X | CHRF10 | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 7am – 10pm daily | 1hr STAT upon receipt of sample at UWMC Lab 4hrs ROUTINE |
| factor X level (Not used for anticoagulant monitoring) |
F10 | 2ml or 3ml blue top tube | 7:30am to 3pm Mon-Fri | 4 hrs ROUTINE |
Anti-Xa Activity (Heparin Activity)
Heparin Monitoring with Anti-Xa Activity (HIXA)
Used to monitor heparin activity and more accurately reflects the specific amount of heparin effect than PTT. Click here to see UW Medicine’s Heparin Infusion Using AntiXa Monitoring Protocol.
The therapeutic range for IV unfractionated heparin: 0.3-0.7 units/mL
LWMH Monitoring with Anti-Xa Activity (LMWXA)
- routine monitoring is not recommended – there is no “therapeutic range” for LMWH
- dosing adjustments to reach a particular target range are not recommended
- no optimal target range is correlated with efficacy or clinical endpoints
- if measured, check peak anti-Xa level 3-4 hours after a dose
- observed peak anti-Xa levels for q12h dosing of LMWHs (e.g enoxaparin 1mg/kg q12h) = 0.5-1 units/mL
- observed peak anti-Xa levels for 1.5mg/kg q24h dosing of LMWHs (e.g enoxaparin 1.5mg/kg q24h) = 1-2 units/mL
- if measured, check trough anti-Xa level at end of the dosing interval (just before the next dose)
- expected trough anti-Xa levels = < 0.5 units/mL
- higher troughs suggest impaired clearance – an increased dosing interval may be indicated
Apixaban Assay (APIXN1)
Uses chromogenic anti-Xa activity to extrapolate apixaban concentrations in ng/mL. The lower limit of the measurable range is < 20 ng/mL
Apixaban levels may be helpful to obtain for patients with recent apixaban exposure requiring transition to unfractionated heparin because the presence of apixaban interferes with heparin anti-Xa levels. Refer to UW Medicine’s DOAC to Heparin Transition Guidelines for more information.
Apixaban levels are not recommended prior to invasive procedures as a method of ensuring absence of drug.
Instead, for the following situations, measuring a DOAC Screen may be helpful to:
- assure the absence of drug prior to invasive procedures
- assure the absence of drug prior to the use of thrombolytic therapy
For apixaban, no “therapeutic range” has been established. Observed peak and trough concentrations of patients exposed to therapeutic dosing are described below. (Source)
| Apixaban Dose | Observed Peak Concentration | Observed Trough Concentration |
|---|---|---|
| VTE Prophylaxis | ||
| 2.5mg bid | 41-146 ng/ml | 23-109 ng/ml |
| VTE Treatment | ||
| 2.5mg bid
5mg bid 10mg bid |
30-153 ng/ml
59-302 ng/ml 111-572 ng/ml |
11-90 ng/ml
22-177 ng/ml 41-335 ng/ml |
| Stroke Prevention in AF | ||
| 2.5mg bid
5mg bid |
69-221 ng/ml
91-321 ng/ml |
34-162 ng/ml
41-230 ng/ml |
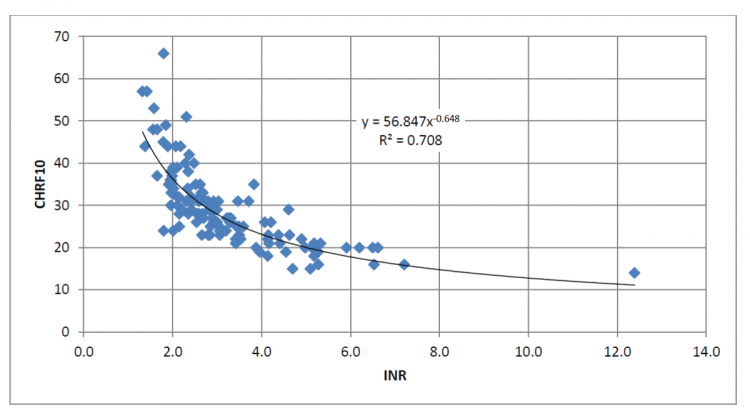
Chromogenic Factor X (CHRF10)
Used instead of INR to monitor warfarin in patients bridged with direct thrombin inhibitors that might interfere with INR.
In rare cases, strong lupus inhibitor/antiphospholipid antibodies might also interfere with PT/INR, in which case chromogenic factor X levels may be used as an alternative monitoring strategy. If there is a concern for an inhibitor, a PT 1:1 mixing study can help determine if an inhibitor is present. Otherwise, INR should be used as the default monitoring strategy. For patients with newly diagnosed APS treated with warfarin, INR values (measured on the OUTPATIENT instrument that will be used for chronic treatment) should be checked for correlation with factor X activity.
- The therapeutic range for warfarin: INR 2-4 ~ CFX 35% – 25%
Dabigatran Assay (DABIGL)
Uses plasma dilute thrombin time (see below) to extrapolate dabigatran concentrations in ng/mL. The lower limit of the measurable range is < 50 ng/mL
Measuring the presence of dabigatran may be helpful to:
- assure the absence of drug prior to invasive procedures
- assure the absence of drug prior to the use of thrombolytic therapy
Measuring the presence of dabigatran is less likely to be useful to:
- assess compliance
- assess possible over-anticoagulation in cases of hemorrhage
- assess possible under-anticoagulation in cases of treatment failure
For Dabigatran, no “therapeutic range” has been established. Observed peak and trough concentrations in patients exposed to therapeutic dosing are outlined below. (Source)
| In patients receiving dabigatran 150mg bid | Observed Serum concentrations1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak values | 64 – 443 ng/ml | |||
| Trough values | 31 – 225 ng/ml |
Direct Oral Anticoagulant Screen (DOASP1)
Used to rapidly identify patients who may be taking direct oral anticoagulants. Two tests are performed: the thrombin time (TTPAT) will detect direct thrombin inhibitors (units of measure in seconds) and the Direct Xa Inhibitor Screen (DOXAS) will detect the presence or absence of direct Xa inhibitors (reported as positive/negative). Available rapidly and sent as part of the Emergency Stroke Panel to screen for the presence of anticoagulants.
Measuring DOAC Screen may be helpful to:
- assure the absence of drugs prior to invasive procedures
- assure the absence of drugs prior to the use of thrombolytic therapy
Direct Thrombin Inhibitor Assay (DTI) 1
(Plasma-Diluted Thrombin Time)
Used instead of aPTT to monitor injectable DTI therapy. Preferred over aPTT due to better sensitivity, and is not affected by antiphospholipid antibodies. Cost, turn-around time and 24/7 availability at UWMC are similar to aPTT.
- The therapeutic range for DTIs administered by continuous infusion
- For argatroban: 60-100 seconds
- For bivalirudin: 60-90 seconds
- For lepirudin: 90-160 seconds
Fondaparinux Assay (FNDXT)
Uses chromogenic anti-Xa activity to extrapolate serum concentrations of fondaparinux in mcg/mL.
There is no “therapeutic range” for fondaparinux, and dosing adjustments to reach a particular target or goal range are not recommended. Observed peak and trough levels from clinical trials, based on the dose administered, are described below.
| Fondaparinux dose | Observed Peak Concentrations (3 hours after dose) |
Observed Trough Concentrations (24 hours after dose) |
|---|---|---|
| VTE Prophylaxis (2.5mg) | Mean (1): 0.39 and 0.5 mcg/ml Range (2): < 0.042-1.161 mcg/ml |
Mean (1): 0.14 and 0.19 mcg/ml Range (2): < 0.042-0.569 mcg/ml |
| VTE Treatment | Mean (3): 1.2 and 1.26 mcg/ml Ranges (4): |
Mean (3): 0.46 and 0.62 mcg/ml Ranges (4): |
| 5mg (< 50kg) | 0.685 - 1.522 mcg/ml | 0.242 - 1.003 mcg/ml |
| 7.5mg (50-100 kg) | 0.206 - 2.95 mcg/ml | 0.048 - 2.023 mcg/ml |
| 10mg (> 100 kg) | 0.582 -1.713 mcg/ml | 0.0.081 - 1.041 mcg/ml |
(1) mean concentrations in PENTHIFRA and PENTATHLON clinical trials, as noted in the package insert
(2) range of concentration values from these trials (data on file, GSK)
(3) mean concentrations in MATISSE DVT and MATISSE PE trials, as noted in the package insert
(4) range of concentration values from these trials (data on file, GSK)
INR Point-of-Care Testing (Rapid INR; PRORPD)
Whole blood INR testing using point-of-care devices is available for eligible patients at UW Neighborhood Clinics. Home INR testing devices using similar technology are available for eligible patients through certain third-party companies.
UWMedicine Anticoagulation Services does not routinely use whole blood INR testing, and does not recommend whole blood INR testing in the following circumstances:
- patients initiating warfarin who have not yet reached a steady state and a stable maintenance dose
- patients with variable responses to warfarin and/or frequent warfarin dose adjustments
- patients with goal INR upper limit greater than 3.5
- patients with known HCT< 30.0 (INRatio/Alere) or HCT < 25.0 (Coaguchek/Roche) or HCT > 55.0
- patients with ventricular assist devices (LVAD)
- patients undergoing weekly INR testing prior to/following cardioversion or ablation
- patients with end-stage renal disease and/or on hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis
- patients with chronic inflammatory conditions (eg: rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, hepatitis, diabetic nephropathy, glomerulonephritis)
- patients with acute inflammatory conditions (ex. acute viral infection, acute bacterial infection including sepsis)
- patients with advanced malignancy
- patients with known chronic elevated fibrinogen for any reason
- patients with known antiphospholipid antibodies (lupus anticoagulant, anti -beta-2-glycoprotein I, anticardiolipin antibody)
- patients exposed to an injectable direct thrombin inhibitor in the last 24 hours (argatroban, bivalirudin)
- patients exposed to an injectable heparin product in the last 48 hours (heparin, dalteparin, enoxaparin)
- patients exposed to an injectable factor Xa inhibitor in the last 5 days (fondaparinux)
- patients transitioning between warfarin and any direct oral anticoagulant (apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, rivaroxaban)
- self-testing in patients during the first three months of warfarin therapy
- self-testing in patients who are non-compliant with follow-up or non-adherent to medication administration
Rivaroxaban Assay (RIVAR1)
Uses chromogenic anti-Xa activity to extrapolate rivaroxaban concentrations in ng/mL. The lower limit of the measurable range is < 25 ng/mL
Rivaroxaban levels may be helpful to obtain for patients with recent rivaroxaban exposure requiring transition to unfractionated heparin because the presence of rivaroxaban interferes with heparin anti-Xa levels. Refer to UW Medicine’s DOAC to Heparin Transition Guidelines for more information.
Rivaroxaban levels are not recommended prior to invasive procedures as a method of ensuring absence of drug.
Instead, for the following situations, measuring a DOAC Screen may be helpful to:
- assure the absence of drug prior to invasive procedures
- assure the absence of drug prior to the use of thrombolytic therapy
For rivaroxaban, no “therapeutic range” has been established. Observed peak and trough concentrations in patients exposed to therapeutic dosing are outlined below 1,2
| Stroke Prevention in AF (20mg daily) | VTE Treatment (20mg daily) | VTE Prevention (10mg daily) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak values | 160 – 360 ng/ml | 175 – 360 ng/ml | 91 – 196 ng/ml |
| Trough values | 4 – 96 ng/ml | 19 – 60 ng/ml | 1.3 – 38 ng/ml |
1. Mueck W et al. Population pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of once- and twice-daily rivaroxaban for the prevention of venous thromboembolism in aptients undergoing total hip replacement. Thromb Haemost 2008; 100:453-61.
2. Buller HR et al. A dose-ranging study evaluating once-daily oral administration of the factor Xa inhibitor rivaroxaban in the treatment of patients with acute symptomatic deep vein thrombosis. The Einstein DVT Dose Ranging Study. Blood 2008; 112:2242-2247.