Throughout my experience participating in the Our Climate Action group, I have acquired new skills that enhanced my learning. My project members and I participated in multiple listening sessions run by other fellows from the Our Climate activists explaining the Evergreen New Deal: a comprehensive climate change reform policy that will introduce greener solutions to current predicaments. All of this exposure to the bits and bolts of how our state and country runs in regards to introducing laws and regulations has added to my sense of citizenship and provided me with a clearer path to contribution. Before this experience, I felt like I was staring at the system from a distance, and it was too entangled in itself for me to get involved.
One interactive portion of our activism involved spreading a survey to Washingtonians under the age of 30 focused on collecting opinions on what prominent complications must immediately be addressed in our direct environment here in the state. During role in lobbying to Tina Orwall, spreading the voices of concerned residents, I especially made an emphasis on how COVID-19 should not get in the way of climate change policy because the underprivileged community is affected negatively by both COVID and climate change, and these two issues interacting creates an even bigger obstacle.
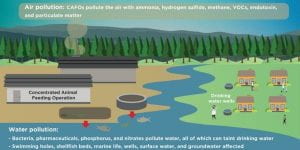
Climate change is obviously a complicated interconnected system woven through everything from our bodies interaction to the weather, to how our climate changes drastically in the atmosphere. There’s an undeniable chain of consequences between our climate and food. For example, “As reserves are depleted, changes in production would have a bigger impact on the price of food….Scientists have warned hotter temperatures and more erratic rainfall could increase the frequency and intensity of droughts (Reuters).” Droughts will affect how much food is yielded and therefore affect how people will be able to sustain themselves globally. Learning about connections between climate change and the food system, as well as climate change and COVID-19, it was easy for me to realize that underprivileged communities are not only affected by certain disadvantages individually, but also how all those disadvantages come together and create increased adverse challenges. This is why climate change needs to be addressed among the other issues, taking out one factor of damage out at a time, we can salvage what, and who, we are hurting and destroying.
Please watch this short animation on how climate change interacts with the causes and consequences of other global dilemmas: